Applications of 3D Scanning in the Automotive Industry
3D scanning is the process of capturing 3D geometric data of an object using a scanning device and developing that data into a digital copy for further analysis. Depending on the use case scenario, 3D data can be used for various purposes. Several 3D scanners and 3D data processing software have evolved to deliver high precision and accuracy down to 10 microns that have eventually found their way into almost all areas of the automobile sector right from design, production, inspection, and service to aftermarket support. In this article, we will look at some of the top applications of how 3D scanning is helping the automotive industry not only in manufacturing but also in the aftermarket.

Design
Automotive design and styling studios use clay modeling and digital sculpting tools for creating new car concept models. After creating the prototype clay model, it is scanned using a 3D scanner to create a digital model. The scanning software converts the raw point data into a suitable format that is supported by CAD software. Class-A surface design tools are then used for defining each surface of the CAD model accurately. Once the CAD design is complete, it serves as the blueprint for all downstream engineering and manufacturing processes.
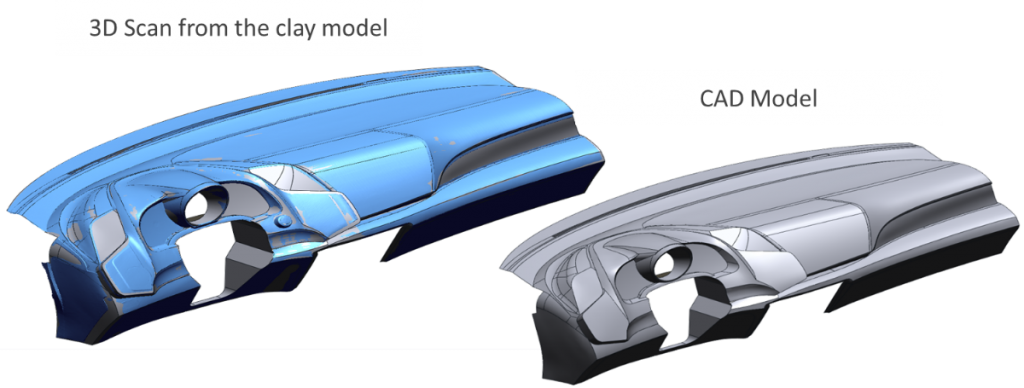
Benchmarking and Reverse Engineering
Benchmarking is the process of analyzing the designs of other car models and car parts and arriving at the best possible combination in terms of the performance needed. There are companies that exclusively do these jobs of scanning and reverse engineering the parts of an entire car with the help of 3D scanners. Design teams can make use of these digital replicas to analyze, benchmark, perform virtual teardown and value engineering to enhance the existing designs and come up with better designs.
Restoration
If any automotive part is not available locally, it can be produced with 3D printing without the need for complex tooling. And to do so, 3D scanning can be utilized. Today’s 3D scanners are capable of producing accurate details of the part that allow for exact replication with 3D printing. And not just 3D printing, but even for small batch production methods such as casting and machining too would need the design details of the part. 3D scanning is a great way in such scenarios in the creation of CAD models.
Customization
Creating custom internal features that suit the style and personality of the customer is a new trend that has evolved around automotive enthusiasts and sporting events. The part that needs to be redesigned is first scanned with 3D scanning and using that as a template, design variations are made such as a new dashboard, rear spoilers, rooftop mounts, custom seats, etc.
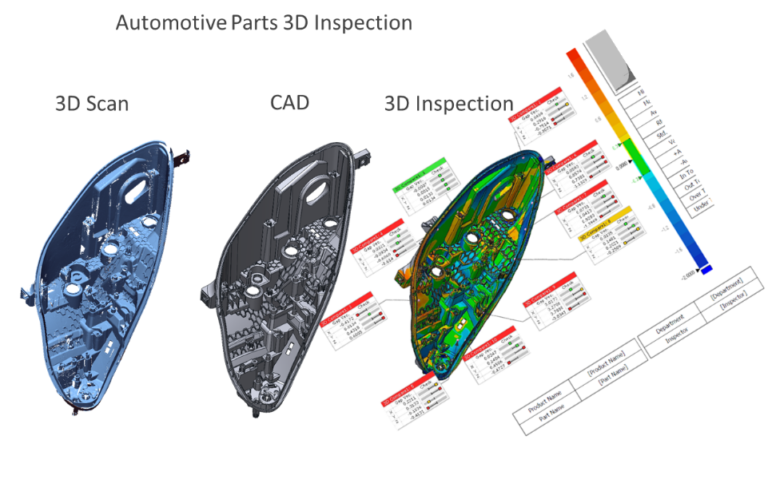
Inspection
With the availability of metrology-grade industrial 3D scanners, it is possible to scan a given part and compare the dimensions with a reference model. This has enabled companies to evaluate the precision and accuracy of outsourced components and then verify if they fit well in the car or not.
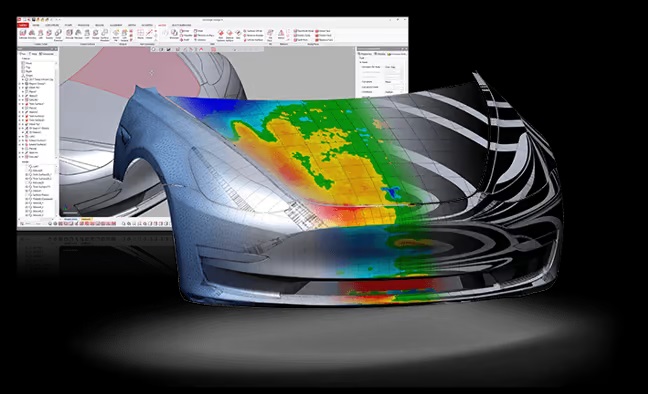
Quality Assurance
Although there are several contact-type quality inspection tools for checking the dimensional accuracy of the parts produced, they are not always suitable for verifying complex geometries that have curved surfaces. Hence there are dedicated 3D scanning tools from ScanTech that allow engineers to not only generate the scanned surfaces but can also give deviation reports and full-color plots from an original CAD file. The portability and speed of the scanners pose as a versatile alternative to coordinate measuring machines.
One reply on “Applications of 3D Scanning in the Automotive Industry”
I want to buy this 3d printer machine