MULTI JET fusion (mJf)
- FDM technology can go about building quick prototypes with strength and speed, at a very economical price in a range of thermoplastic materials, which makes it a very attractive option.

Digital Manufacturing
Turn your ideas to reality with our full fledged 3D Printing, CNC Machining, Casting & Molding service capabilities. Our facility is equipped with entire range of 3D Printing technologies, 10 CNC Machines, 2 Injection Molding Machines and have a passionate team to serve you.
Quick Online Quote
Upload files in Get Quote section and get quote within 4 hrs
Technical Competency
Technically qualified team in various mfg. technologies
Competitive Pricing
Highly competitive price and bulk discounts also available
NDA & IP Protection
All designs and data are kept in highly secure private server
Overview
3D printing utilizing the extrusion of thermoplastic material is easily the most common and recognizable 3DP process. The most popular name for the process is Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM).
The process works by melting plastic filament that is deposited, via a heated extruder, a layer at a time, onto a build platform according to the 3D data supplied to the printer. Each layer hardens as it is deposited and bonds to the previous layer. The FDM/FFF processes require support structures for any applications with overhanging geometries.
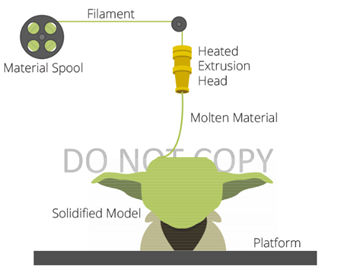
The great advantage of FDM is the durable materials it uses, the stability of their mechanical properties over time, and the quality of the parts. The production-grade thermoplastic materials used in FDM are suitable for detailed functional prototypes, durable manufacturing tools and low-volume manufacturing parts.
Support structures, or lack thereof, have generally been a limitation of the entry level FFF 3D printers. However, as the systems have evolved and improved to incorporate dual extrusion heads, it has become less of an issue. Occasionally, the process can be slow for some part geometries and layer-to-layer adhesion can be a problem, resulting in parts that are not watertight.
Applications
- Prototypes for form, fit and function testing
- Prototypes directly constructed in production materials like ABS, Nylon
- Low-volume production of complex end-use parts
- Patterns for Sand casting & molds with lesser detailing
materials
PLA
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
ABS
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
PETG
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
Nylon
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
Poly Carbonate
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
Wood
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
Flexible
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
HIPS
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
PVA
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | Flexural Strength(MPa) | Impact Strength(MPa) | Melting Temperature°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 62.63 | 65.02 | 4.28 | 190 – 220 |
specifications
Minimum Wall thickness: 1.2 mm
Minimum details size: 2 mm (for text/ hole diameters etc)
Layer thickness: 0.1 mm – 0.3 mm
Max dimensions: 650 x 600 x 600 mm. Large parts can be created with assembling individual parts by interlocking designs or glueing together.
Standard Accuracy: ± 0.3% (with lower limit on ± 0.3 mm).
Lead Time: Minimum 2 working days for despatch
Surface finish: visible layers with texture.
post processing
Basic: Support Removal, Sanding, Smoothing
Add on: Primer, Coating/ Painting
Clients

Think3D has been a great partner for us in supplying COVID-19 test cartridges on-time despite the pandemic challenges. When we came up with a new requirement needing a workforce of more than 25 people, think3D took up the challenge and arranged the workforce within 2 days. I highly recommend think3D for any manufacturing needs.
Sanket Srivatsav
Production In-Charge, Molbio

As a professor doing research on new materials, I needed a strong industry partner to assist us. think3D perfectly fit that bill. think3D team is highly knowledgeable on all manufacturing technologies and the team is very prompt in responding to all our requests. My research has been very successful, thanks to think3D team.
Dr. Karthik Chetan V
Asst. Professor, BITS Pilani

We found issue with one part at the time of assembly and needed a quick replacement. think3D team has quickly responded to our request, redesigned the part and printed it using metal 3D Printing and delivered in 3 days time. The part came out really well and the design was better than that of the actual one.
Rama Krishna
Senior Manager (IMM), BDL




























Frequently Asked Questions
FDM stands for Fused Deposition Modeling, which simply means that material is deposited in single layers that fuse together to create a 3D object.
Stereolithography (SLA) printing was first invented in the 1980’s and works by curing resin with light. The light solidifies a liquid resin via a process called photo-polymerization and builds objects layer by layer.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is the process of turning digital designs into three-dimensional objects.During SLS, tiny particles of plastic, ceramic or glass are fused together by heat from a high-power laser to form a solid, three-dimensional object.
3D Printers and 3D Printing: Technologies, Processes and Techniques. 3D printing is also called additive manufacturing. This term accurately describes how this technology works to create objects. “Additive” refers to the successive addition of thin layers between 16 to 180 microns or more to create an object.
There are some common denominators, for example, both use a laser to trace out and build individual layers. For SLA a liquid resin is cured, where as in SLS powder is selectively fused together.
Because the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy.
To create your 3D print, a laser in the printer melts the powder together. So here’s how it works: A super-thin layer of Aluminum or Titanium powder is spread out by a roller. The print chamber of the 3D printer is then heated up.
The Powder Bed Fusion process includes the following commonly used printing techniques: Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), Electron beam melting (EBM), Selective heat sintering (SHS), Selective laser melting (SLM) and Selective laser sintering (SLS).
MJP or MultiJet Printing is an inkjet printing process that uses piezo printhead technology to deposit either photocurable plastic resin or casting wax materials layer by layer. MJP is used to build parts, patterns and molds with fine feature detail to address a wide range of applications.
PolyJet is a powerful 3D printing technology that produces smooth, accurate parts, prototypes and tooling. With microscopic layer resolution and accuracy down to 0.1 mm, it can produce thin walls and complex geometries using the widest range of materials available with any technology.
One reply on “MJF”
you have 3d printing house services also available…?